 The initialization process after the RAID is configured
Oct 12, 2023
The initialization process after the RAID is configured
Oct 12, 2023
For parity RAID, after the RAID parameters are set on the RAID card and the RAID Settings are applied, all the disks in the RAID array need to be initialized. The time required is related to the number and size of the disks. The larger the disk, the more there are, and the longer it will take.
Consider:
What does a RAID card write to disk? You can think about a new disk just out of the factory, is there any data on it?
Yes. What data? It's either all zeros or all ones. Here, all zeros refer to the actual data part, except for some special positions such as sector headers. Because the magnetic region on the disk has two states, either the n-pole or the S-pole. So that means it's either 0 or 1, and there can't be a third state. So what about these 0's or 1's?
Of course, these magnetic regions don't have a chaotic state between 0 and 1. If we do RAID5 with a few disks, but do not change any data on the disks, let's see what state we will be in at this point, say 5 disks, 4 data disk space, 1 parity disk space, on the same strip, 4 data blocks, 1 parity block, and all the data on the blocks are all 0, then if we calculate RAID5, It's true, because 0 XOR 0 XOR 0 XOR 0 XOR 0 XOR 0=0, right.
If you start with all 1's, then similarly 1 XOR 1 XOR 1 XOR 1 XOR 1 XOR 1=1, also true. However, if RAID5 is made of 6 disks, and the initial values are all 1, the situation is contradictory. 1 XOR 1 XOR 1 XOR 1 XOR 1 XOR 1 XOR 1 =0, in which case the correct result would be that the parity block is 0, but the initial disk is all 1, and the parity block data is also 1, which contradicts the calculation.
If the initialization process doesn't make any changes to disk and we just write data, for example, we write a piece of data to the second extend, changing 1 to 0, and then the controller validates the data according to the formula: parity data for new data = (old data EOR new data) EOR. (1EOR 0) EOR1=0, and the new parity is 0, so the final data looks like this: 1 XOR 0 XOR 1 XOR 1 XOR 1 XOR 1. We figured it out to be equal to 1, but the RAID controller figured it out to be 0, so there's a contradiction.
Why did you make this mistake? That's because the RAID controller didn't start with a proper data relationship in the first place, and the parity data of the parity block was inconsistent with the data block at the beginning, which led to more and more errors. So after the RAID controller is set up and enabled, in the process of initialization, it needs to write 0 or 1 for each sector of the disk, and then calculate the correct parity bit, or do not change the data of the data block, directly use these existing data, recalc the parity block data of all strips. On this basis, new incoming data will not be misrepresented.
Tip: For products such as NetApp, RAID groups do not need to be initialized and are available immediately. Even adding disks to a RAID group that already has data does not cause any additional IO. Because it will reset all Spare disks, that is, send a Zero Unit SCSI instruction to the disk, and the disk will automatically perform the zero. For RAID groups made from these disks, there is no validation and therefore no initialization, or waiting for the disks to clear to zero.
Unleash the power of data! Classic reliability, innovative evolution - RAID Card brings you beyond imagination performance and reliability. Whether you are an individual user, an enterprise, or a data center, our RAID cards will provide you with unparalleled data protection and high-speed transfer. STOR Technology Limited provides original and new cloud storage products, such as megaraid sas 9341 8i, lsi 9361 8i 2gb, lsi megaraid 9460 8i, etc., welcome to consult.
 Experience RAID at its Best! Discover the unbeatable performance and reliability of the 9560-8i
Jan 12, 2024
Experience RAID at its Best! Discover the unbeatable performance and reliability of the 9560-8i
Jan 12, 2024
 Maximize Efficiency with 9460-8i—Experience faster data management and file access.
Jan 09, 2024
Maximize Efficiency with 9460-8i—Experience faster data management and file access.
Jan 09, 2024
 Get information on the model number of the network card
Jan 04, 2024
Get information on the model number of the network card
Jan 04, 2024
 Ideal for External Storage Connectivity: 9300-8e
Dec 30, 2023
Ideal for External Storage Connectivity: 9300-8e
Dec 30, 2023
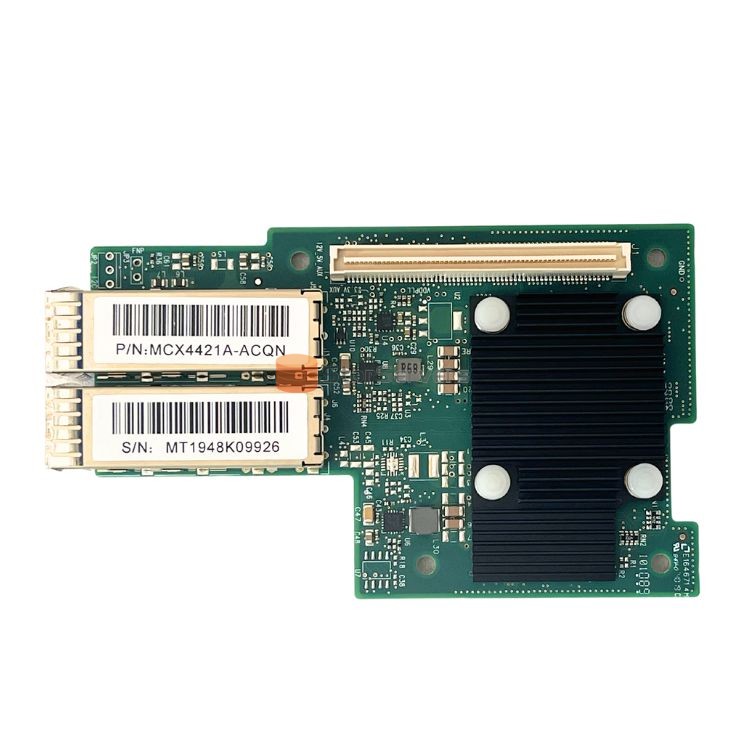 Application of MCX4421A-ACQN high performance network adapter
Dec 16, 2023
Application of MCX4421A-ACQN high performance network adapter
Dec 16, 2023
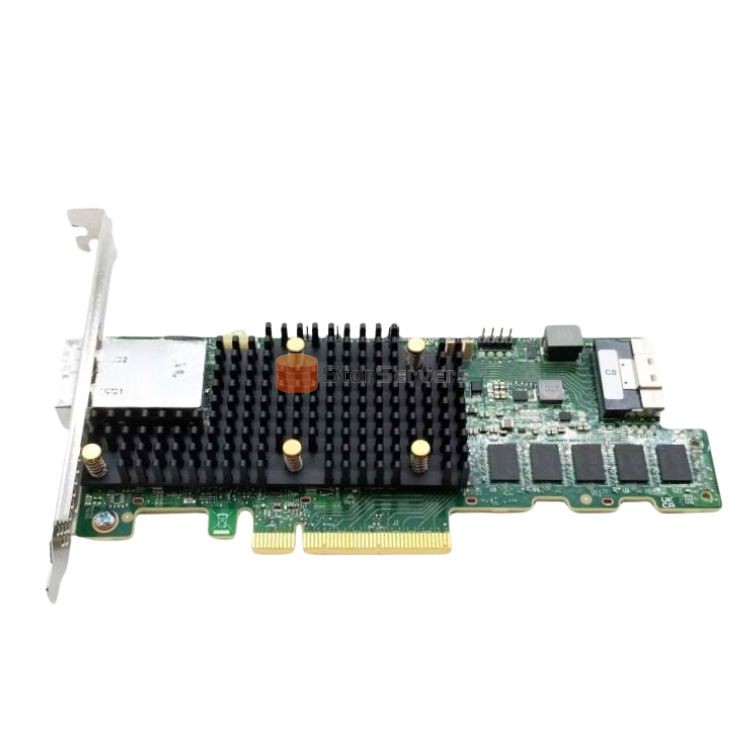 MegaRAID 9580-8i8e Key Features
Dec 06, 2023
MegaRAID 9580-8i8e Key Features
Dec 06, 2023
 The speed and reliability of today's storage technology
Nov 22, 2023
The speed and reliability of today's storage technology
Nov 22, 2023
 Introduction and Installation of 9440-8i Raid Card
Nov 17, 2023
Introduction and Installation of 9440-8i Raid Card
Nov 17, 2023
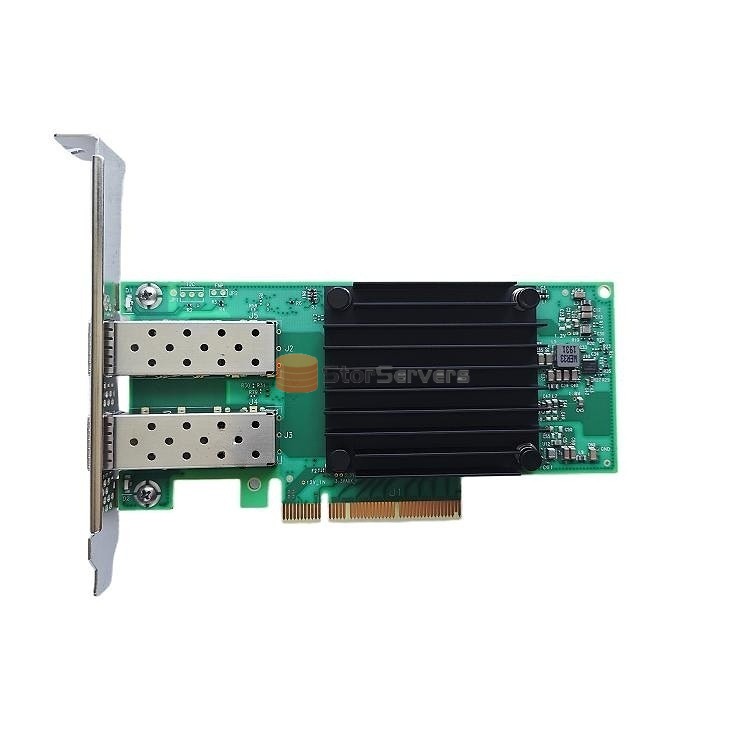 This section describes the MCX512A-ACAT Network adapter
Nov 09, 2023
This section describes the MCX512A-ACAT Network adapter
Nov 09, 2023
 Port type of the RAID card
Nov 08, 2023
Port type of the RAID card
Nov 08, 2023
 Three minutes,Tell you the difference between SAS and SATA
Nov 02, 2023
Three minutes,Tell you the difference between SAS and SATA
Nov 02, 2023
 The initialization process after the RAID is configured
Oct 12, 2023
The initialization process after the RAID is configured
Oct 12, 2023